The Yahoo Services has a serious SQL Injection FlawProof of ConceptTime-line of the vulnerability
Ebrahim had now discovered a flaw in the Yahoo service which allows SQL Injection. Once the SQL injection is initiated, the particular Yahoo service can be exploited by a potential attacker to Remote Code Execution and Escalated to Root Privilege on one of Yahoo servers.
Proof of Concept
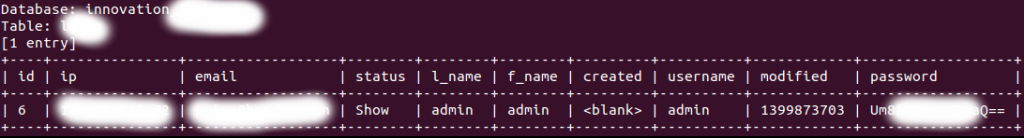
As explained in his blog post, Ebrahim started his research with the Yahoo Service domain: https://innovationjockeys.yahoo.net/. While examining this particular domain with HTTP POST requests he noticed something that could be exploited for SQL Injection attack. In Ebrahim’s own words, https://innovationjockeys.net/tictac_chk_req.php POST: f_id=9631 After a few manual tests and with the use of SQLMap, the hacker confirmed the presence of a flaw in the Yahoo system: https://innovationjockeys.net/tictac_chk_req.php POST: f_id=-9631? OR (2777=2777)# Available Databases: [] information_schema [] innovation******* #Hiding dbnames for Yahoo privacy. [] web*** Ebrahim could read the data stored in the database with SQL Injection attack and once he got the the the administrator credentials from the database he was able to decode them despite it was encoded as Base64.
2- I found the Administrator Password stored in the database and it was encoded as Base64
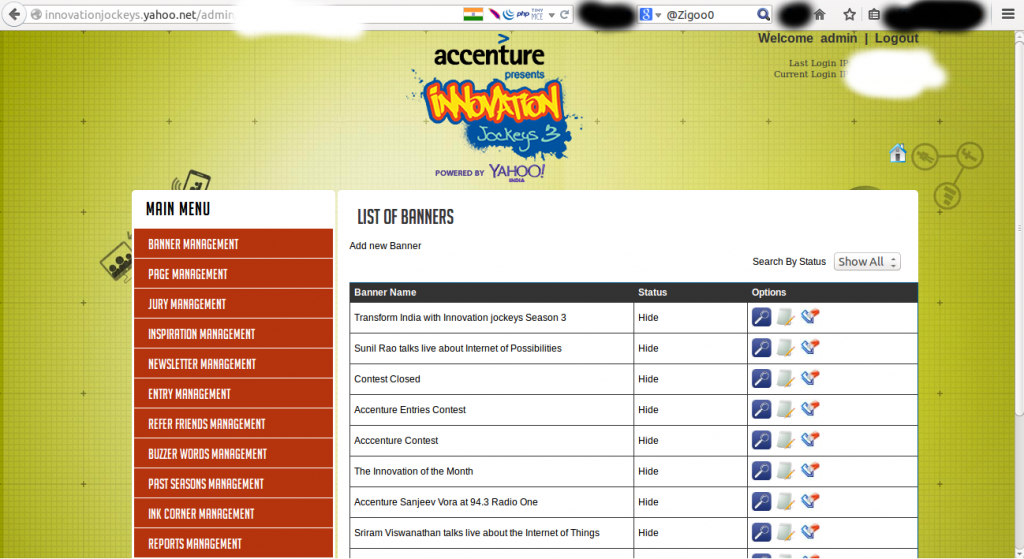
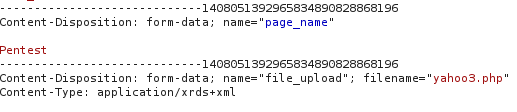
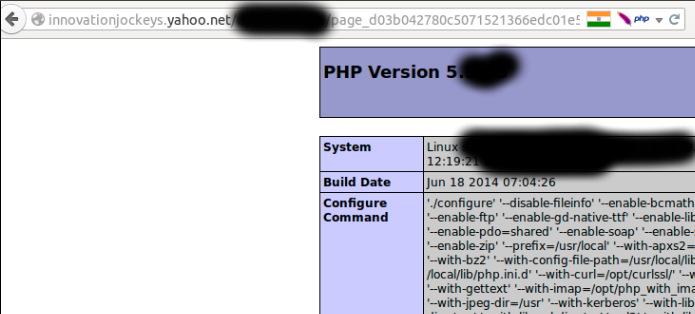
Once he had access to the admin panel, he tried to trigger a Remote Code Execution uploading his content. Inspecting the uploading request, the expert discovered the cause of the problem in the “Content-Type” Header!
Renaming the “Content-Type” Header to be “application/php” the problems was solved.
Ebrahim submitted the Proof of Concept to Yahoo and Yahoo patched the vulnerability. Surprisingly, Yahoo declined to award any bounty to Ebrahim
Time-line of the vulnerability
2014-09-05 Initial report to Yahoo 2014-09-06 Yahoo confirmed the vulnerability 2014-09-07 Yahoo Fixed the Vulnerability 2014-09-19 Yahoo told Ebrahim that this vulnerability is not eligible for a reward!!!